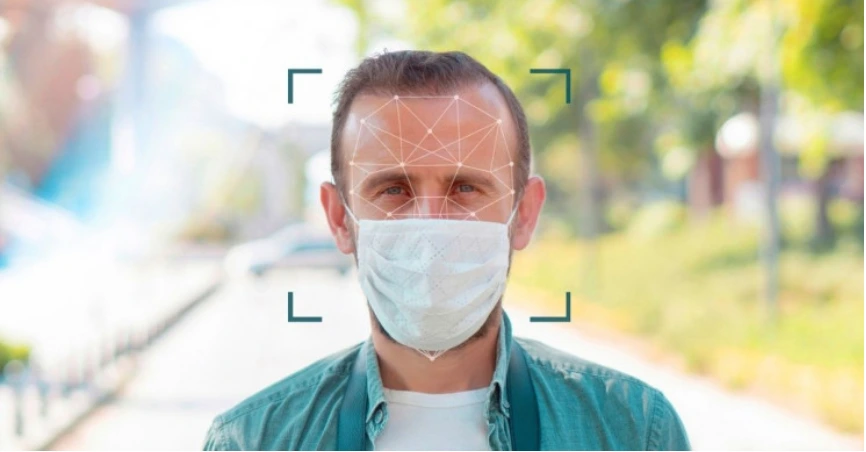
Can Face recognition tech identify you while wearing a face mask?
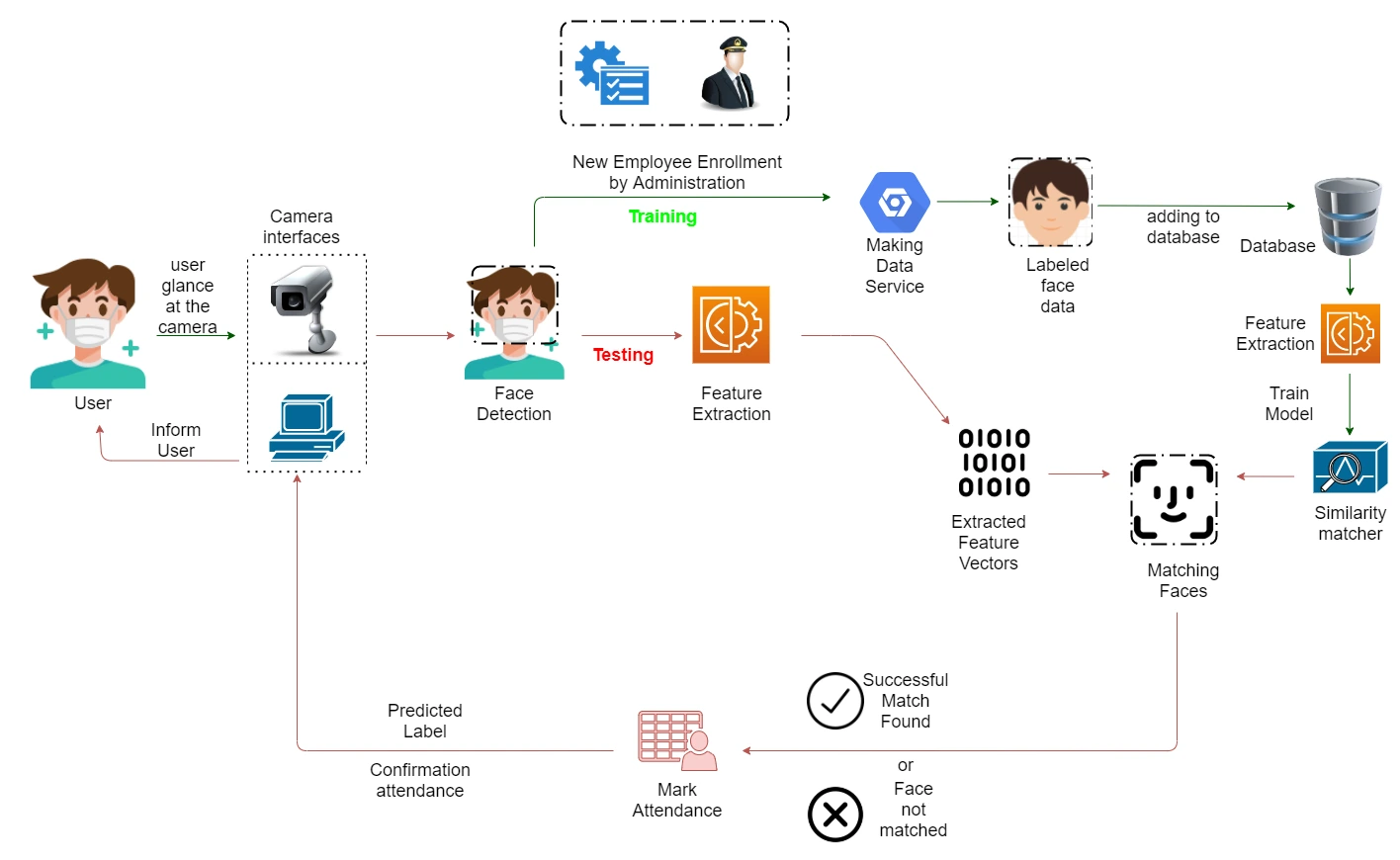
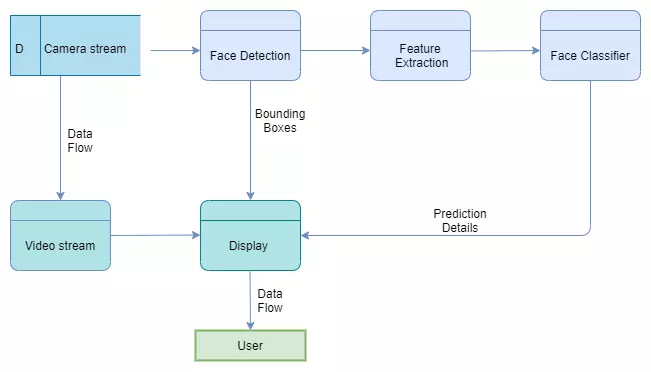
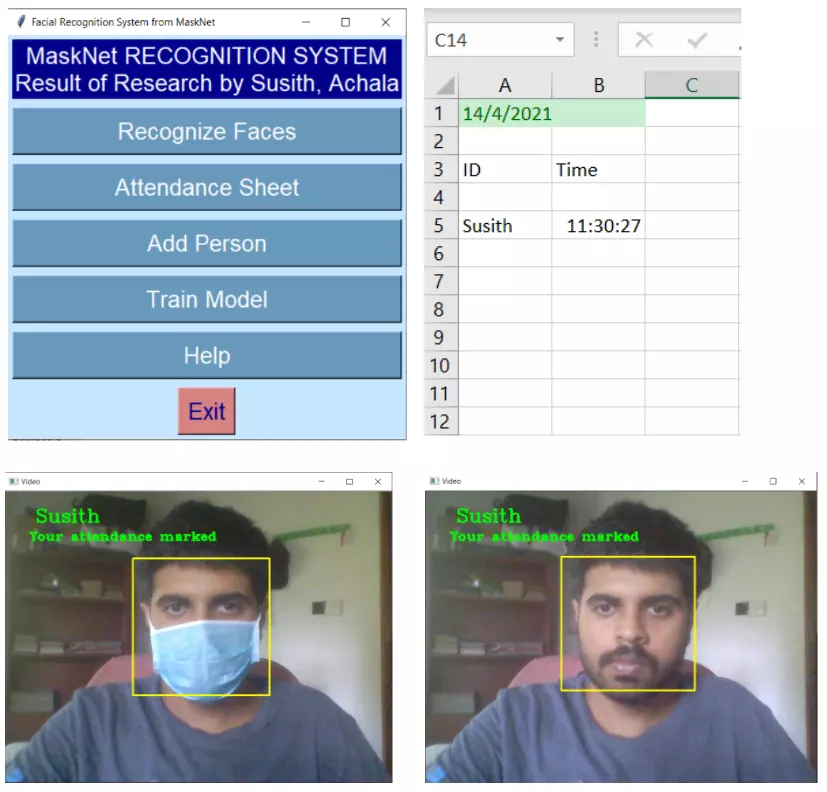
Recognizing faces while wearing a face mask is considered the most difficult facial occlusion challenge because it occludes a large area that usually covers around 60% of the frontal face which contains rich features including the nose and mouth. This is emerging problem which higlighted during the pandemic period. I was able to develop a appropriate solution to overcome the above issue through a research study. The developed occlusion invariant face recognition system is published as a open work to the public.
Rapid development and breakthrough of deep learning in the recent past have witnessed the most promising results from face recognition algorithms. But they fail to perform far from satisfactory levels in the unconstrained environment during the challenges such as varying lighting conditions, low resolution, facial expressions, pose variation and occlusions (Wen et al., 2016). Among the challenges, Occlusion is one of the most challenging problems faced by current face recognition algorithms. Moreover, Face mask makes higher inter-class similarity and inter-class variations due to covering a large area of the face which tricks the facial verification. process of face recognition systems (Guo and Zhang, 2019). Ongoing Face Recognition Vendor Test (FRVT) (Ngan, Grother and Hanaoka, 2020) is a performance evaluation report based on 89 face verification algorithms while wearing face masks (Ngan, Grother and Hanaoka, 2020). The study (Damer et al., 2020), concludes their results on the effect of wearing a face mask which given strong points of performance degradation on face recognition systems, showing the necessity of the development of mask capable face recognition systems.
Facial recognition has been studied for several years and it’s a longitudinal & preliminary task in computer vision (Best-Rowden and Jain, 2018). Among the biometrics, methodologies face recognition has a better edge on the accuracy, efficiency, usability, security, and privacy to recognize the identity non-intrusively. Furthermore, Facial recognition is widely preferred over potential candidates because of its contactless authentication behaviour which helps to keep good hygiene practices.(Zeng, Veldhuis and Spreeuwers, 2020). Face recognition is widely used in personal device log-on, passport checking, ATMs, border control, forensics, law enforcement, surveillance, and national security (Ejaz et al., 2019).

The study, by (Damer et al., 2020) concludestheir evaluationsidentified strong signs of an adverse effect of face masks on existing face recognition algorithms and occlusion invariant face recognition algorithms, pointing out the failure of them to identify faces while wearing a mask and the necessity of developing appropriate face recognition solutions. Furthermore, Ongoing Face Recognition Vendor Test (FRVT) is a performance evaluation report based on 89 face recognition algorithms on masked faces. If the mask covers around 70% of the occluded area most algorithm’s failure rate is increased by 20% to 50% according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology, United States (Ngan, Grother and Hanaoka, 2020).
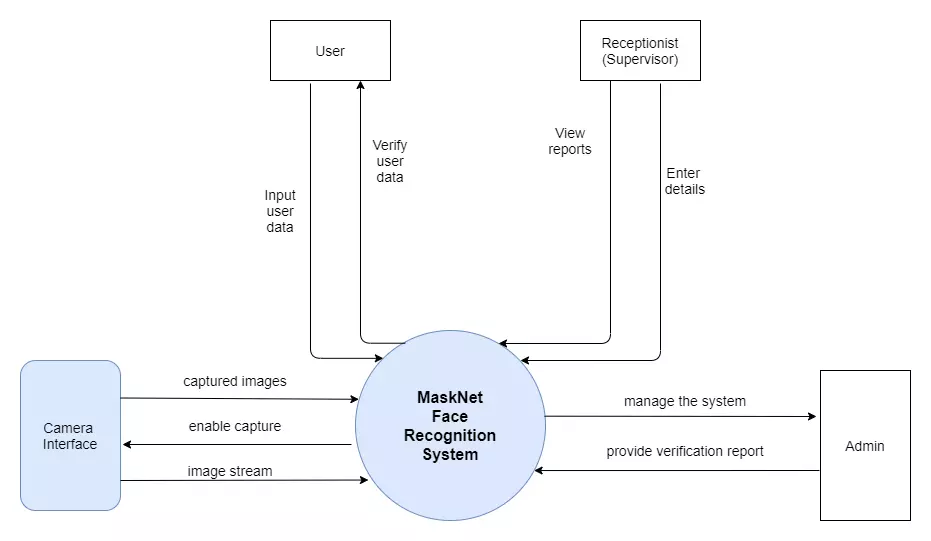
The recent surveys on the effect of face mask occlusion on face recognition precisely illustrate that existing face recognition systems and occlusion invariant face recognition systems are failed to handle face mask occlusions. However, most of the work done in small occlusions such as spectacles, sunglasses and partial captures commonly appears in in-the-wild capture conditions. In the existing research literature, there are few efforts are focused to handle face mask occlusions that are not met expected accuracy, efficiency, usability and security. This research is focused on building an effective novel facial recognition algorithm with the capability of recognizing faces while wearing a face mask in real-time to overtake barriers of occlusion invariant face recognition with growing incentives of wearing face masks without reducing well-known qualities of facial recognition.